
Topics
At a glance: Isometry
2020-04-14
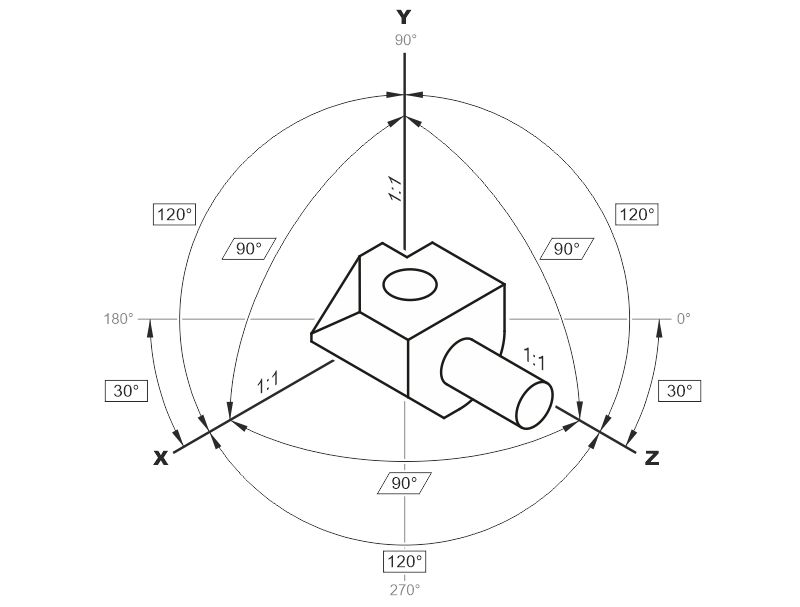
In isometry, the object is placed in front of a projection plane so that the three main axes X, Y, Z result in a projected opening angle of 120°.
Although isometric projection may appear distorted by the parallel projection beams in the case of large, flat objects, it has many other advantages:
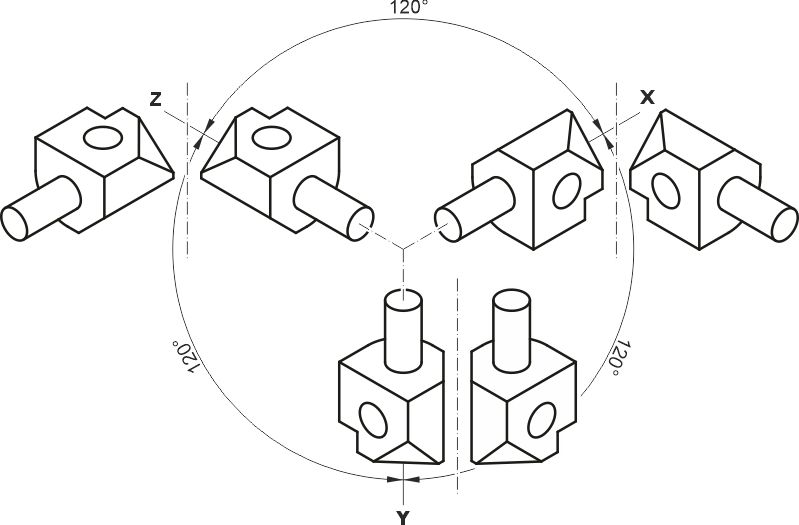
- Due to the identical angle between the main axes of 120°, an object once drawn can be used in different views by rotating and mirroring.
- Since none of the axes has a shortening factor, it is easy to measure or at least to recognize length ratios in the illustration.
- Very good editability due to parallel projection, i.e. parallel edges in reality are also parallel in the illustration.
- Broad support by symbol libraries.
- Optimal visibility from three sides of the illustration object.